Deep varicose veins are a very unpleasant and quite dangerous pathology of the venous vessels of the circulatory system.
Deep varicose veins of the lower limbs are a pathology that extends into the blood vessels that pass through the muscular structure of the legs.The lengthening and dilation of venous vessels significantly impairs blood flow and contributes to the development and progression of thrombi.
The danger of this disease is that blood clots that form in the walls of blood vessels are likely to break off and be transported to the pulmonary arteries.
When this disease occurs, the veins undergo an irreversible process of lengthening and dilation.As the process progresses, vein walls are observed to thin and form nodes, preventing the free transport of blood through the vessels.
Most commonly, people aged 30-40 years and above are susceptible to this disease.
Causes of deep varicose veins of lower limbs
The occurrence and development of the disease may be caused by a variety of adverse factors.Deep varicose veins are the result of severe disturbances in the circulatory process in one part of the lower limbs.
As the disease progresses, patients may develop trophic ulcers at sites where circulation is interrupted, which may trigger the development of gangrene, a condition that requires amputation of the affected limb part.
In addition, varicose veins can cause muscle deformation in the lower extremities and form blood clots, which may then detach and travel to the pulmonary arteries, leading to death.
The main factors leading to the occurrence and progression of the disease are as follows:
- There is a genetically determined genetic predisposition leading to congenital lesions and weakening of the cells lining the veins;
- Gender - Women are more susceptible to illness than men, which is related to hormonal changes during pregnancy, the onset of menopause and the use of hormonal medications and contraceptives;
- When the body is in an upright position for a long time and is overweight, the patient's venous pressure increases due to reduced mobility and increased static overload;
Additionally, the cause of the disease may be:
- Periodically increase the load on the limbs.
- Immune system function is severely disrupted.
- When wearing tight shoes, there is constant pressure on the blood vessels in the legs.
- Being overweight or obese.
- Development of various forms of dermatitis.
- Consequences of surgical intervention.
- Subject the lower extremities to increased static loads.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
In addition, cellulite can lead to the development of pathology.
Seeing a qualified phlebologist when the disease is first suspected can allow you to identify the disease promptly.
Main symptoms of deep varicose veins
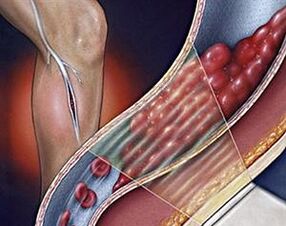
Most often, in the initial stages of disease progression, the disease manifests itself as a slight feeling of fatigue in the legs after prolonged static loading or prolonged walking.Additionally, there will be slight swelling of the tissues in the limbs during this period.
Most often, symptoms of these diseases appear at the end of the day and gradually disappear with prolonged rest.When these signs appear, it is necessary to consult a phlebologist and conduct specialized studies to identify and clarify the presence of pathology.
The use of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods allows us to determine the extent of the disease and to decide on timely and adequate treatment options for the disease.As the disease progresses further, it enters more advanced stages, which are characterized by a constellation of signs and symptoms characteristic of progressive disease.
The advanced stage of pathology is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- Severe pain in the legs in the evening and at night;
- Persistent soft tissue swelling and lower extremity heaviness;
- Persistent soft tissue swelling leading to increased limb size;
- Patients often experience cramps in their lower legs, which most often occur at night;
- The skin of the affected areas of the extremities appears bluish;
- When physical pressure is exerted on the legs, pathologically affected venous vessels may appear on the feet, thighs, and calves.
Further progression of the disease leads to the appearance of small wounds, which do not heal for a long time and subsequently transform into trophic ulcers.
Without adequate and timely treatment, the progression of the disease can be fatal to the patient.The progression of varicose veins leads to a gradual deformation of the muscle structure and negative changes in the skin and bone.
As the disease progresses over time, patients may develop eczema symptoms and develop trophic ulcers, which may eventually develop into gangrene.This can lead to sepsis or death.
In venous vessels affected by varicose veins, the process of thrombosis occurs.As a result of this process, a blood clot forms that is able to break apart and be transported through the circulatory system.
When a blood clot travels to the pulmonary artery, it can become blocked, causing death.
Basic diagnostic methods
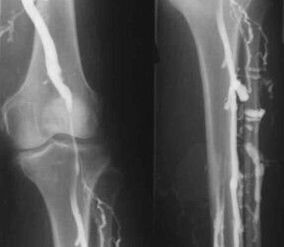
An experienced phlebologist can determine the presence of varicose veins in the deep veins of the lower limbs through characteristic symptoms, clearly visible even in photos of the legs, but the method of treatment for this disease is chosen individually after a detailed examination of the patient and taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient's body.
To determine the presence and stage of development of the disease, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used.Laboratory methods include general blood and urine testing.
The most common instrumental diagnostic method is the use of ultrasound to examine the venous blood vessels in the legs.This technology allows you to visualize the vascular system and determine the degree of progression of pathological processes.
In addition, if necessary, the attending physician will prescribe:
- Venography.
- Photoplethysmography.
Blood volume in the veins of the lower extremities can be determined using venous occlusion plethysmography.
Appropriate treatment is prescribed to the patient only after a thorough examination and results are available.
Modern medicine offers a variety of options for treating the disease—drugs, nondrugs, and surgery.
In the meantime, you can use alternative and traditional treatments at home after consulting your doctor.
Treatment of deep varicose veins
The most reliable way to treat this disease is surgery.Medical treatments using tablets, specialized ointments, topical gels, etc. can be complementary and are actually supportive care.
The use of pharmacotherapy involves the use of several types of drugs during treatment - anticoagulation, anti-inflammatory, venous tone and fibrinolysis
Anticoagulants thin the blood and prevent blood clots from forming.Anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve the inflammatory process in the walls of the veins.Intravenous supplements help increase the tone of the vein walls, and fibrinolytics help dissolve small clots and help clean the venous bed.
Symptoms of the disease, such as swelling, usually disappear due to the use of the drug; in addition, an improvement in superficial skin conditions is also observed.The main condition for using the drug is strict compliance with the doctor's recommendations and the dosage of the drug.
For complete cure of varicose veins, surgical intervention is recommended.
In addition, in the absence of positive dynamics during medical treatment, surgical methods can be used.
The most common pathological surgical treatments are:
- Sclerotherapy;
- phlebectomy;
- Laser coagulation.
Sclerotherapy involves the use of a special substance - a sclerosing agent - during surgery, which is introduced into the lumen of the affected vein and causes the walls of the vessel to bond.This surgery removes venous vessels from the circulatory system, thereby preventing the progression of lesions.The technology is rarely used when severe forms of the disease are detected.
Phlebectomy involves removal of the affected area of venous blood vessels.Most commonly, this method is used to identify superficial venous lesions, but in some cases it is also suitable for the treatment of deep venous vessels in the extremities.
Laser coagulation is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed using a laser; it allows you to remove the affected area of the vein from the circulatory system by bonding the vein walls under the influence of laser radiation.This treatment is nearly painless and does not require a long recovery period, resulting in the most positive feedback from patients.
With surgical treatment, you can completely get rid of the characteristic symptoms of deep varicose veins.The choice of surgical technique depends on the extent of pathology, individual characteristics of the patient, and is performed by the attending physician.

















